
Surgery may be necessary for severe fractures such as fractures of the growth plate or the joint. Immobilization for 6 to 10 weeks is recommended for more serious fractures. A splint or cast may be required for 3 to 4 weeks for a stable buckle fracture. For severe angled fractures, in which the bones have not broken through the skin, your doctor will align the bones properly without the need for surgery (closed reduction). Your child’s doctor will advise you to apply an ice pack over a thin towel on the affected area for 15-20 minutes 3-4 times a day, to relieve pain and swelling. The treatment of forearm fractures in children is based on the location, type of fracture, degree of bone displacement and its severity.
Popping or snapping sound during the injuryįorearm fractures in children can be diagnosed by analyzing X-ray images of the wrist, elbow or the forearm. Inability to turn or rotate the forearm. What are the symptoms of forearm fractures?Ī fractured forearm causes severe pain and numbness. What are the causes of forearm fractures?įorearm fractures in children are caused due to a fall on an outstretched arm or direct hit on the forearm, which may result in breakage of one or both bones (radius and ulna). Fracture occurring at or across the growth plate (Growth plate fracture). Fractured ulna and dislocated head of the radius (Monteggia fracture). Fracture affecting the upper or lower portion of the bone shaft (Metaphyseal fracture). Displacement of the radius, and dislocation of the ulna at the wrist where both bones meet (Galeazzi fracture). One side of the bone breaks and bends the bone on the other side (Greenstick fracture). A stable fracture that compresses the bone on one side, forming a buckle on the opposite side of the bone, without breaking the bone (Buckle or torus fracture). The common types of fractures in children include: Fractures may be “open” where the bone protrudes through the skin, or “closed” where the broken bone does not pierce the skin. What are the different types of forearm fractures?įorearm bones may break in many ways. Thus, if a fracture is suspected in a child, it is necessary to seek immediate medical attention for proper alignment of the bones. The healing of fractures in children is quicker than that in adults. The growth plate, which is made of cartilage (flexible tissue) is present at the ends of the bones in children and helps in the determination of length and shape of the mature bone. 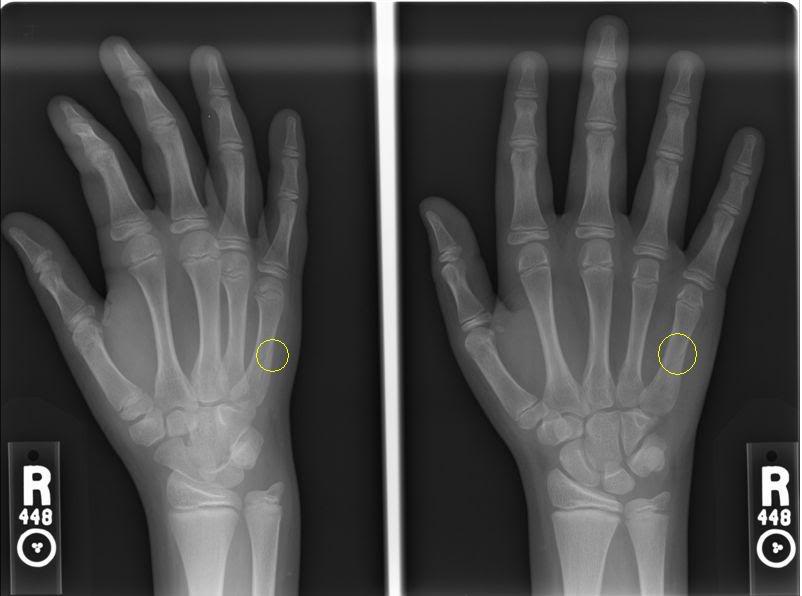
Apart from this, the bones in children are prone to a unique injury known as a growth plate fracture.


Forearm fractures can occur near the wrist, near the elbow or in the middle of the forearm. The radius (bone on the thumb side) and ulna (bone on the little-finger side) are the two bones of the forearm.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
